-
Cryptocurrencies
-
Exchanges
-
Media
All languages
Filecoin is a token on IPFS, and Filecoin is a way to reward miners by contributing idle hard drives. Filecoin uses a brand new algorithm (Proof of Work). In simple terms, if you have a hard drive capacity, the more Filecoin rewards you get.
What is IPFS?
The full name of IPFS is Inter Planetary File System, which is generally translated as "Interstellar File System". It is proposed by Protocol Lab and is a point-to-point (P2P) distributed file system.
However, although it is a file system and a technology used to store data, IPFS is more precisely a transmission protocol. IPFS regards HTTP as an opponent and promotes it to benchmark HTTP, and HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol) is the most commonly used transmission protocol at present. If we want to find the content we want on the Internet, we need to enter the URL, which mostly starts with HTTP. HTTP is transferred through domain name, IP and multiple central servers, and then upload and download files. The achievements of HTTP are irreplaceable, and now we rely on HTTP when we access the Internet. However, HTTP also has some problems, such as not very high performance efficiency, over-reliance on central servers and backbone networks, etc.
In comparison, IPFS is a multi-centered solution. Content addressing is not through domain names or IPs, but through a unique HASH key. IPFS is a distributed file storage system. File data is not stored in a centralized server, but is stored in all computers that meet the criteria on the network.
Of course, IPFS is not only that, but also has many other features, and its levels and application scope also exceeds simple P2P downloads.
There is an incentive mechanism in IPFS - Filecoin. Participants (miners) can receive cryptocurrency Filecoin rewards by contributing storage space and bandwidth.
The relationship between IPFS and Filecoin
Although IPFS has been hot for three or four years, many people still do not understand the concept of IPFS and Filecoin and their relationship. Many people confuse IPFS and Filecoin. "IPFS mining" and "IPFS mining machines" are typical wrong statements.
Protoco Lbas, also known as Protoco Lab, was founded in the San Francisco Bay Area in May 2014 and was founded by Juan Benet, a Stanford University graduate. Juan Benet, a Californian American, graduated from Stanford University, a world-renowned university with a master's degree in computer science. He once co-founded a mobile AR gaming company (Loki Studios) with his partners, which was later acquired by Yahoo. He then moved into StartX, a nonprofit startup accelerator at Stanford University, where he started his entrepreneurial career. In 2014, he founded the IPFS project and received investment from his alma mater. In January 2015, the official version of the IPFS project was released.
IPFS and Filecoin are both projects created by protocol labs. IPFS is a peer-to-peer, versioned, and content addressed hypermedia transmission protocol, targeting the traditional Internet protocol HTTP, and what it wants to build is a distributed web 3.0.
But IPFS is just an open source underlying communication protocol for the Internet, and everyone can use it for free. Currently, all IPFS nodes provide storage space and also need other nodes to help them store resources.
In essence, IPFS transforms the original on-demand download of P2P software into long-term storage of resources. Long-term storage requires service quality assurance, otherwise no user is willing to store their valuable data or resource content that requires service quality assurance into IPFS. So for a loose IPFS network, the user's arbitrary exit, the uncertainty of network quality, the uncertainty of storage geographical location, the uneven performance of hardware resources, and the performance jitter of hardware resources. These problems make IPFS unable to store resource storage that has strong demand for service quality, in other words, it is impossible to use it in the commercial field.
Therefore, IPFS uses Filecoin's incentive mechanism to attract a group of professional storage service providers to provide more professional, secure and stable storage services.
Filecoin is a decentralized storage network based on IPFS. It is the only incentive layer on IPFS and a token issued based on blockchain technology. Miners in the FIlecoin network can obtain FIL by providing storage and retrieval services to customers. Instead, customers can store or distribute data by spending FIL to hire miners.

Filecoin promotes the development of IPFS through economic incentive mechanisms. At the same time, the Filecoin network also needs IPFS to provide ecological support for the development of its market.
The more IPFS network is used, the greater the demand for Filecoin; the more miners there are in Filecoin, the greater the support for IPFS network. Therefore, IPFS and Filecoin form a symbiotic relationship.
Filecoin was born to support the development of IPFS, and IPFS also needs Filecoin to enrich its ecosystem. The more IPFS is used, the greater the demand for Filecoin; the more miners there are in Filecoin, the greater the support for IPFS.
The role of FIL
Filecoin is a decentralized distributed storage network, the only incentive layer for IPFS. Filecoin uses the blockchain token system to issue Token, referred to as FIL.
Filecoin builds a decentralized storage trading market based on the IPFS protocol, including two markets: "storage" and "retrieval". This market runs on a blockchain with a local protocol token (FIL), where miners can obtain FIL by providing storage to customers; similarly, customers can hire miners to store or distribute data by spending FIL.
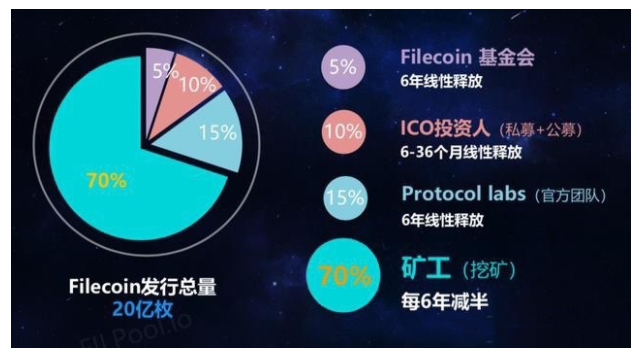
FIL token allocation plan
Filecoin uses the blockchain token system to issue Token, referred to as FIL, with a total issuance of 2 billion yuan, and the allocation plan consists of four parts:
Miners: 70% (i.e. 1.4 billion), released linearly through block rewards, and halved every 6 years;
Team: 15% (i.e. 300 million pieces), as the R&D and operating expenses of the protocol laboratory team, will be released linearly in 6 years;
Investors: 10% (i.e. 200 million), allocated to investors participating in private and public offerings, and released linearly in 6-36 months;
Foundation: 5% (i.e. 100 million), as long-term community construction, network management and other expenses, will be released linearly in 6 years;
Filecoin consensus mechanism
FileCoin innovative development adopts a hybrid consensus mechanism - Proof of Replication (PoRep) + Proof of Time (PoSt) + Expected Consensus.
Proof of Copy (PoRep): Proof of Copy is a new type of storage proof. Storage miners need to prove to the verifier that they store the corresponding data on a specific device, rather than storing multiple copies of data on one device. Filecoin uses copying to effectively prevent witch attacks, outsourcing attacks, and proxy attacks.
Spatial-time proof (PoSt): The space-time proof is based on the copy proof, plus timestamp and other technologies to obtain a proof of miners storing data over a period of time. Even if the user is not online, he can use space-time proof to verify the data stored by the miner during that period of time at some point in the future. PoSt is generated by Filecoin when verifying miners to store user data. Filecoin converts the current storage ratio of miners in the network to the miner's voting power of the miner, and reuses PoSt to generate consensus.
Expected Consensus (EC): Filecoin's consensus protocol is built on Proof-of-Stake, and the stake in the stake is replaced with storage. In each cycle, there are expected to be one leader miner, but in some cases, multiple leader miners will be elected. The elected miners create new blocks and broadcast the new blocks to the network, thereby obtaining block rewards. The goal is to make the miner's interest in block production proportional to his or her contribution to storage.
Filecoin miners' income sources
More people pay attention to Filecoin because 70% of tokens are released through mining, but many people still have some misunderstandings about Filecoin's mining income.
What we call mining is actually a process of minting, that is, the network releases tokens through block rewards, and then the tokens will be circulated, traded and used, and miners will gradually start to have storage and retrieval income.
Just like Bitcoin, early miners received block rewards through mining, and then Bitcoin was gradually accepted by more people and began to be widely circulated and traded. Currently, nearly 300,000 transactions are transferred on-chain every day. In addition to block rewards, Bitcoin miners also have miner fees, that is, the income from transaction fees.
So, in the early stages of the development of Filecoin network, miners were encouraged to contribute their servers to build distributed storage networks through block rewards. When the infrastructure of Filecoin network is built and the security and stability of the network reaches a certain level, more and more institutions and individuals will begin to store their data on the servers of Filecoin network, and miners will start to generate storage mining benefits.
As the Filecoin network stores more and more real data, a search demand will naturally occur, and miners will have the benefits of searching and mining.
Introduction to Filecoin Space Race
Filecoin space race officially started at 6 a.m. Beijing time on August 25. According to the space race rules released by Filecoin, the basic structure of the competition is: within three weeks, miners will compete with each other to provide as much storage capacity as possible for the network. The top 100 miners in the world and the top 50 miners in each continent will receive Filecoin rewards based on the amount of storage they implement on the network during the test period.
Miners can get more rewards in two ways:
1. The size of the reward fund pool increases with the increase of the total network storage capacity.
2. The total fund pool of rewards is strictly distributed according to the proportion of mining contributions, depending on the proportion of their increased storage capacity to the total network storage.
In short, the space competition compares computing power, and the higher the computing power ranks, the more rewards you can get in the later stage. There are actually three channels for getting more rewards. One is to unlock the reward fund pool in the region where you are located to a higher amount, the other is to calculate the proportion of computing power to the overall computing power of the network, and the last is to deploy machines on other continents.
At the Filecoin miners' meeting held on July 22, the official further clearly proposed the selection criteria for incentive competitions: original storage capacity, transaction success rate (more than 80%), and sector life cycle. In addition, the 100,000 new FIL rewards will be ranked according to the entire network block and refer to the reward structure of the main network.
On September 15, the first phase of the Filecoin space race was successfully concluded. With the end of the first phase of the space race, the official announced the opening of the second phase.
Simple understanding of the space competition, the first stage is a computing power competition, and it is not based on how much Fil is mined as the standard. The second stage is a packaging competition, which competes with packaging capabilities and repair strength. This is also related to the overall operation and maintenance capabilities of miners, which is very important. The second phase may be more intense than the first phase.
According to data from the first phase of the competition, the global effective computing power reached 230 PiB, successfully unlocking 1.5 million FIL rewards worldwide; the node storage success rate is 86%, and the data retrieval success rate is 98%.











